Introduction
Overview of the Topic
Throughout history, communication has played a vital role in society. As technology continues to advance, new methods of communication have emerged, making it easier for people to connect and share information. Alongside traditional forms of communication, such as face-to-face conversations and written letters, we now have communication tools like email, instant messaging, and social media platforms. These new methods have transformed the way we interact with each other and have had a significant impact on both personal and professional relationships.
The Importance of Effective Communication
Effective communication is crucial in every aspect of our lives. Whether it’s in the workplace, within families, or in social settings, being able to convey ideas, opinions, and emotions in a clear and concise manner is essential. It helps build strong relationships, resolves conflicts, ensures understanding, and facilitates collaboration. Without effective communication, misunderstandings can occur, leading to confusion, frustration, and even strained relationships.
Face-to-Face Communication vs. Digital Communication
Advantages of Face-to-Face Communication
Face-to-face communication refers to direct interaction between individuals, where they can see and hear each other in real-time. While digital communication has become the norm in today’s technologically advanced world, face-to-face communication still offers several advantages:
- Non-verbal cues: Body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice are important elements of communication that can only be fully observed in face-to-face interactions. These cues can enhance understanding and help convey emotions.
- Immediate feedback: In-person communication enables participants to receive immediate feedback, allowing for clarifications and adjustments during conversations.
- Building trust: Face-to-face interactions foster a sense of trust, as individuals can directly observe and assess each other’s credibility and sincerity.
Advantages of Digital Communication
Digital communication refers to the exchange of information through electronic devices, such as emails, text messages, and video calls. It offers its own set of advantages:
- Convenience: Digital communication allows individuals to communicate with others regardless of their geographical location, making it easier to stay connected.
- Efficiency: Messages can be sent and received instantaneously, increasing efficiency and reducing response times.
- Accessibility: With the widespread use of smartphones and internet access, digital communication provides accessibility and convenience at any time and from anywhere.
Choosing the Right Communication Method
Consider the Context
When deciding which communication method to use, it’s essential to consider the context and purpose of the interaction. The following factors can help determine the most appropriate method:
- Urgency: If the information needs to be conveyed promptly, digital communication methods like instant messaging or phone calls may be more suitable.
- Complexity: For complex or sensitive conversations, face-to-face communication can help ensure clarity and minimize misunderstandings.
- Personal Preference: Some individuals may have a preference for certain communication methods based on their comfort level and familiarity.
Combining Methods
In many cases, a combination of communication methods can yield the best results. For instance, important information can be initially shared through digital means to provide documentation, followed by face-to-face discussions to address any questions or concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective communication is vital for successful personal and professional relationships. While face-to-face communication offers the advantages of non-verbal cues and immediate feedback, digital communication provides convenience and efficiency. Choosing the right communication method depends on the context and purpose of the interaction, and often a combination of methods can lead to optimal results. By understanding and utilizing various communication tools, individuals can enhance their ability to connect and collaborate effectively.
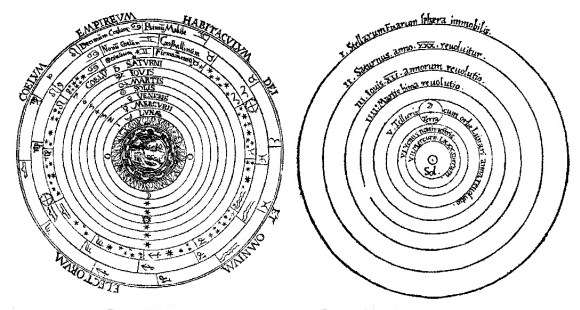
The Concept of Heliocentrism
The Copernican Revolution
The idea of heliocentrism, where the Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun, is known as one of the most significant revolutions in the field of astronomy. This concept, also known as the Copernican Revolution, challenged the prevailing belief that the Earth was the center of the universe. Instead, it proposed that the Sun was at the center, and all other celestial bodies orbited around it.
The Contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer in the 16th century, was the one who first put forward the heliocentric model of the solar system. His book, “De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium” (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), published in 1543, presented his findings and mathematical calculations supporting the heliocentric theory. Copernicus’s work paved the way for further research and exploration in the field of astronomy.
Advantages of the Heliocentric Model
The concept of heliocentrism offered several advantages over the previously accepted geocentric model. Here are some of the key benefits:
– Simplicity and elegance: The heliocentric model simplifies the movements of celestial bodies, explaining their motions in a more elegant and straightforward manner.
– Explanation of planetary retrograde motion: The heliocentric model can explain the retrograde motion of planets, where they appear to move backward in the sky temporarily. This phenomenon was a challenge for the geocentric model, but it can be easily explained in the heliocentric model using the varying speeds of planets.
– Predictive accuracy: The heliocentric model, with its accurate calculations and predictions, was able to accurately predict planetary positions and movements. This made it a valuable tool for navigation and timekeeping.
Comparison Between Heliocentrism and Geocentrism
| Heliocentrism | Geocentrism |
|---|---|
| Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun. | Earth is the center of the universe, and everything revolves around it. |
| Accurately explains planetary retrograde motion. | Difficult to explain planetary retrograde motion. |
| Simplifies the movements of celestial bodies. | The motions of celestial bodies are more complex. |
| Provides accurate predictions of planetary positions. | Predictive accuracy is limited. |
In Conclusion
The concept of heliocentrism revolutionized our understanding of the universe and our place in it. This shift in perspective had profound implications for astronomy, physics, and our overall understanding of the natural world. The heliocentric model’s simplicity, predictive accuracy, and ability to explain planetary motions made it a more scientifically and mathematically sound explanation than the geocentric model. Today, heliocentrism is widely accepted as the accurate representation of our solar system and the basis of modern astronomy.
Significance of the Heliocentric Theory
Revolutionizing Our Understanding of the Universe
The concept of heliocentrism, with its revolutionary idea that the Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun, has had a profound impact on our understanding of the universe. This shift in perspective, also known as the Copernican Revolution, challenged the traditional belief that the Earth was the center of the universe and paved the way for a new era of astronomical knowledge and exploration.
The Contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus
The heliocentric theory was first proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus, a 16th-century Polish astronomer. In his groundbreaking book, “De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium”, he presented detailed calculations and evidence supporting the idea that the Sun, not the Earth, was at the center of the solar system. Copernicus’s work laid the foundation for further scientific discoveries and provided a framework for future astronomers to build upon.
Advantages of the Heliocentric Model
The heliocentric model offers several advantages over the previously accepted geocentric model. Its simplicity and elegance make it a more logical and straightforward explanation for the movements of celestial bodies. Additionally, the heliocentric model provides a clear understanding of planetary retrograde motion, a phenomenon that was difficult to explain with the geocentric model. Furthermore, the accuracy of the heliocentric model’s predictions made it an invaluable tool for navigation and timekeeping.
Comparison Between Heliocentrism and Geocentrism
| Heliocentrism | Geocentrism |
|---|---|
| Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun. | Earth is the center of the universe, and everything revolves around it. |
| Accurately explains planetary retrograde motion. | Difficult to explain planetary retrograde motion. |
| Simplifies the movements of celestial bodies. | The motions of celestial bodies are more complex. |
| Provides accurate predictions of planetary positions. | Predictive accuracy is limited. |
In Conclusion
The heliocentric theory has forever changed our understanding of the universe. By shifting our perspective from a geocentric model to a heliocentric model, we have gained valuable insights into the movements and interactions of celestial bodies. Nicolaus Copernicus’s contributions to this theory laid the groundwork for further scientific advancements in astronomy. Today, the heliocentric model is widely accepted as the accurate representation of our solar system and forms the basis of modern astronomical research. Its simplicity, predictive accuracy, and ability to explain complex celestial motions make it a cornerstone in our quest to understand the vast expanse of the universe.
Historical Background
The Copernican Revolution
The concept of heliocentrism, which proposed that the Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun, was a groundbreaking revolution in the field of astronomy. This theory, also known as the Copernican Revolution, challenged the prevailing belief that the Earth was at the center of the universe. Instead, it suggested that the Sun occupied the central position, and all other celestial bodies orbited around it.
The Contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus
In the 16th century, a Polish astronomer named Nicolaus Copernicus played a pivotal role in introducing the heliocentric model of the solar system. His notable work, “De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium” (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), published in 1543, presented his findings and mathematical calculations in support of the heliocentric theory. Copernicus’s pioneering work paved the way for further exploration and research in the field of astronomy.
Advantages of the Heliocentric Model
The concept of heliocentrism offered several advantages over the previously accepted geocentric model. Here are some key benefits of the heliocentric model:
– Simplicity and elegance: The heliocentric model simplifies the movements of celestial bodies, providing a more elegant and straightforward explanation.
– Explanation of planetary retrograde motion: Unlike the geocentric model, the heliocentric model can easily explain the retrograde motion of planets, where they temporarily appear to move backward in the sky. This phenomenon is attributed to the varying speeds of planets.
– Predictive accuracy: The heliocentric model, with its precise calculations and predictions, was able to accurately forecast planetary positions and movements. This made it a valuable tool for navigation and timekeeping.
Comparison Between Heliocentrism and Geocentrism
| Heliocentrism | Geocentrism |
|---|---|
| Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun. | Earth is the center of the universe, and everything revolves around it. |
| Accurately explains planetary retrograde motion. | Difficult to explain planetary retrograde motion. |
| Simplifies the movements of celestial bodies. | The motions of celestial bodies are more complex. |
| Provides accurate predictions of planetary positions. | Predictive accuracy is limited. |
In Conclusion
The concept of heliocentrism revolutionized our understanding of the universe and our place within it. This paradigm shift had profound implications for astronomy, physics, and our overall comprehension of the natural world. The heliocentric model’s simplicity, predictive accuracy, and ability to explain planetary motions rendered it a more scientifically and mathematically sound explanation than the geocentric model. Today, heliocentrism is widely accepted as the accurate representation of our solar system and forms the basis of modern astronomy.
Historical Background
The Copernican Revolution
The concept of heliocentrism, which proposed that the Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun, was a groundbreaking revolution in the field of astronomy. This theory, also known as the Copernican Revolution, challenged the prevailing belief that the Earth was at the center of the universe. Instead, it suggested that the Sun occupied the central position, and all other celestial bodies orbited around it.
The Contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus
In the 16th century, a Polish astronomer named Nicolaus Copernicus played a pivotal role in introducing the heliocentric model of the solar system. His notable work, “De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium” (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), published in 1543, presented his findings and mathematical calculations in support of the heliocentric theory. Copernicus’s pioneering work paved the way for further exploration and research in the field of astronomy.
Advantages of the Heliocentric Model
The concept of heliocentrism offered several advantages over the previously accepted geocentric model. Here are some key benefits of the heliocentric model:
– Simplicity and elegance: The heliocentric model simplifies the movements of celestial bodies, providing a more elegant and straightforward explanation.
– Explanation of planetary retrograde motion: Unlike the geocentric model, the heliocentric model can easily explain the retrograde motion of planets, where they temporarily appear to move backward in the sky. This phenomenon is attributed to the varying speeds of planets.
– Predictive accuracy: The heliocentric model, with its precise calculations and predictions, was able to accurately forecast planetary positions and movements. This made it a valuable tool for navigation and timekeeping.
Comparison Between Heliocentrism and Geocentrism
| Heliocentrism | Geocentrism |
|---|---|
| Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun. | Earth is the center of the universe, and everything revolves around it. |
| Accurately explains planetary retrograde motion. | Difficult to explain planetary retrograde motion. |
| Simplifies the movements of celestial bodies. | The motions of celestial bodies are more complex. |
| Provides accurate predictions of planetary positions. | Predictive accuracy is limited. |
In Conclusion
The concept of heliocentrism revolutionized our understanding of the universe and our place within it. This paradigm shift had profound implications for astronomy, physics, and our overall comprehension of the natural world. The heliocentric model’s simplicity, predictive accuracy, and ability to explain planetary motions rendered it a more scientifically and mathematically sound explanation than the geocentric model. Today, heliocentrism is widely accepted as the accurate representation of our solar system and forms the basis of modern astronomy.
Historical Background
The Copernican Revolution
The concept of heliocentrism, which proposed that the Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun, was a groundbreaking revolution in the field of astronomy. This theory, also known as the Copernican Revolution, challenged the prevailing belief that the Earth was at the center of the universe. Instead, it suggested that the Sun occupied the central position, and all other celestial bodies orbited around it.
Contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus
In the 16th century, a Polish astronomer named Nicolaus Copernicus played a pivotal role in introducing the heliocentric model of the solar system. His notable work, “De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium” (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), published in 1543, presented his findings and mathematical calculations in support of the heliocentric theory. Copernicus’s pioneering work paved the way for further exploration and research in the field of astronomy.
Advantages of the Heliocentric Model
The concept of heliocentrism offered several advantages over the previously accepted geocentric model. Here are some key benefits of the heliocentric model:
– Simplicity and elegance: The heliocentric model simplifies the movements of celestial bodies, providing a more elegant and straightforward explanation.
– Explanation of planetary retrograde motion: Unlike the geocentric model, the heliocentric model can easily explain the retrograde motion of planets, where they temporarily appear to move backward in the sky. This phenomenon is attributed to the varying speeds of planets.
– Predictive accuracy: The heliocentric model, with its precise calculations and predictions, was able to accurately forecast planetary positions and movements. This made it a valuable tool for navigation and timekeeping.
Comparison Between Heliocentrism and Geocentrism
| Heliocentrism | Geocentrism |
|---|---|
| Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun. | Earth is the center of the universe, and everything revolves around it. |
| Accurately explains planetary retrograde motion. | Difficult to explain planetary retrograde motion. |
| Simplifies the movements of celestial bodies. | The motions of celestial bodies are more complex. |
| Provides accurate predictions of planetary positions. | Predictive accuracy is limited. |
In Conclusion
The concept of heliocentrism revolutionized our understanding of the universe and our place within it. This paradigm shift had profound implications for astronomy, physics, and our overall comprehension of the natural world. The heliocentric model’s simplicity, predictive accuracy, and ability to explain planetary motions rendered it a more scientifically and mathematically sound explanation than the geocentric model. Today, heliocentrism is widely accepted as the accurate representation of our solar system and forms the basis of modern astronomy.
The Heliocentric Model
Historical Background
The Copernican Revolution, which introduced the concept of heliocentrism, was a groundbreaking advancement in astronomy. It challenged the prevailing belief that the Earth was at the center of the universe and proposed that the Sun was the central celestial body, with other planets orbiting around it. Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, played a significant role in this revolution with his work “De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium” in 1543.
Contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus’s work on the heliocentric model laid the foundation for further exploration in astronomy. In his book, he presented mathematical calculations and evidence supporting the Sun as the center of the solar system. His pioneering research revolutionized our understanding of the universe.
Advantages of the Heliocentric Model
The heliocentric model offered several advantages over the geocentric model. These benefits contributed to its wide acceptance and adoption. Some key advantages include:
– Simplicity and elegance: The heliocentric model simplified the movements of celestial bodies, providing a more elegant and straightforward explanation.
– Explanation of planetary retrograde motion: Unlike the geocentric model, the heliocentric model easily explained the retrograde motion of planets. This phenomenon occurs when planets temporarily appear to move backward in the sky, a phenomenon attributed to the varying speeds of planets.
– Predictive accuracy: The heliocentric model’s precise calculations and predictions accurately forecasted planetary positions and movements. This accuracy made it an invaluable tool for navigation and timekeeping.
Comparison Between Heliocentrism and Geocentrism
| Heliocentrism | Geocentrism |
|---|---|
| The Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun. | The Earth is the center of the universe, and everything revolves around it. |
| Accurately explains planetary retrograde motion. | Difficult to explain planetary retrograde motion. |
| Simplifies the movements of celestial bodies. | The motions of celestial bodies are more complex. |
| Provides accurate predictions of planetary positions. | Predictive accuracy is limited. |
In Conclusion
The heliocentric model revolutionized our understanding of the universe and our place within it. Its simplicity, predictive accuracy, and ability to explain celestial motions made it a scientifically and mathematically sound explanation. Today, heliocentrism is widely accepted as the accurate representation of our solar system and forms the basis of modern astronomy. The contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus and the Copernican Revolution paved the way for further advancements and exploration in the field of astronomy.
Key Principles of Heliocentrism
The Copernican Revolution
The concept of heliocentrism, which proposed that the Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun, marked a pivotal moment in the history of astronomy. It challenged the prevailing belief that the Earth was at the center of the universe and introduced a more accurate understanding of our place in the cosmos. The heliocentric model, also known as the Copernican Revolution, revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics and shaped the course of scientific inquiry for centuries to come.
Contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer of the 16th century, played a crucial role in the development and promotion of the heliocentric model. In his groundbreaking work, “De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium” (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), published in 1543, Copernicus presented a comprehensive case for the heliocentric theory. Building upon astronomical observations made by earlier scholars, Copernicus’s mathematical calculations and logical arguments provided compelling evidence for the Sun’s central position in the solar system. His contributions formed the foundation for subsequent advancements in astronomy.
Key Principles of the Heliocentric Model
The heliocentric model introduced several key principles that revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics and astronomy as a whole. Here are some of the fundamental principles of heliocentrism:
– Central position of the Sun: According to the heliocentric model, the Sun occupies the central position in our solar system, with the Earth and other planets orbiting around it. This concept challenged the traditional notion of the Earth as the center of the universe.
– Planetary retrograde motion: The heliocentric model provides a straightforward explanation for the retrograde motion of planets. Retrograde motion refers to the temporary backward movement of planets in the sky as observed from Earth. The varying speeds of planets and their relative positions in their orbits can account for this phenomenon in the heliocentric model.
– Simplification of celestial movements: The heliocentric model simplifies the movements of celestial bodies, offering a more elegant and intuitive understanding of their paths. By considering the Sun as a central gravitational force, it becomes easier to comprehend the motion of planets and other celestial objects.
– Predictive accuracy: One of the major advantages of the heliocentric model is its superior predictive accuracy. Based on precise calculations and mathematical formulas, the heliocentric model allows for the precise forecasting of planetary positions and movements. This predictive accuracy makes the heliocentric model invaluable for practical applications such as navigation and timekeeping.
Comparison Between Heliocentrism and Geocentrism
To further appreciate the significance of the heliocentric model, let us compare it to the previously accepted geocentric model:
| Heliocentrism | Geocentrism |
|---|---|
| Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun. | Earth is the center of the universe, and everything revolves around it. |
| Accurately explains planetary retrograde motion. | Difficult to explain planetary retrograde motion. |
| Simplifies the movements of celestial bodies. | The motions of celestial bodies are more complex. |
| Provides accurate predictions of planetary positions. | Predictive accuracy is limited. |
In conclusion, the introduction of heliocentrism during the Copernican Revolution had a profound impact on our understanding of the universe. Nicolaus Copernicus’s contributions and the subsequent development of the heliocentric model provided a more accurate and elegant explanation for the motions of celestial bodies. The heliocentric model’s simplicity, predictive accuracy, and ability to explain planetary retrograde motion set it apart from the previously accepted geocentric model. Today, heliocentrism remains the foundation of modern astronomy and represents our current understanding of our place in the solar system.
Planetary Motions in the Heliocentric Model
The Revolution of Planets
In the heliocentric model, the planets, including Earth, revolve around the Sun. This concept revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics and provided a more accurate explanation for planetary motions. The heliocentric model, proposed during the Copernican Revolution, challenged the prevailing belief that the Earth was the center of the universe. Instead, it placed the Sun at the center, revealing a more elegant and intuitive understanding of the paths of celestial bodies.
Astronomical Observations and Mathematical Calculations
The heliocentric model was built upon centuries of astronomical observations and mathematical calculations. Nicolaus Copernicus, in his work “De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium,” presented a comprehensive case for the heliocentric theory. He combined his own observations with those of earlier scholars, using meticulous mathematical calculations to support his arguments. By considering the central position of the Sun and the varying speeds and positions of planets, Copernicus provided compelling evidence for the accuracy of the heliocentric model.
Explaining Planetary Retrograde Motion
One of the key advantages of the heliocentric model is its ability to explain planetary retrograde motion. Retrograde motion refers to the temporary backward movement of planets in the sky, as observed from Earth. In the heliocentric model, this phenomenon can be accounted for by considering the varying speeds and positions of planets in their orbits. As a planet moves in its own orbit around the Sun, it may appear to slow down, reverse direction, and then resume its forward motion. This explanation of retrograde motion was a significant breakthrough in our understanding of the movements of celestial bodies.
The Simplicity and Predictive Accuracy of the Heliocentric Model
The heliocentric model offers a more simplified and elegant understanding of celestial movements. By considering the Sun as a central gravitational force, it becomes easier to comprehend the paths of planets and other celestial objects. Additionally, the heliocentric model boasts superior predictive accuracy. Through precise calculations and mathematical formulas, it allows for the accurate forecasting of planetary positions and movements. This predictive accuracy is invaluable for practical applications such as navigation and timekeeping.
A Comparison with the Geocentric Model
To fully appreciate the significance of the heliocentric model, it is helpful to compare it with the previously accepted geocentric model. The geocentric model held that Earth was at the center of the universe, with everything revolving around it. In contrast, the heliocentric model places the Sun at the center, with Earth and other planets orbiting around it. The heliocentric model provides a more accurate explanation for planetary retrograde motion, simplifies the movements of celestial bodies, and offers superior predictive accuracy compared to the geocentric model.
In conclusion, the planetary motions in the heliocentric model, as proposed during the Copernican Revolution, revolutionized our understanding of the universe. By placing the Sun at the center and explaining the movements of planets through mathematical calculations and observational evidence, the heliocentric model provided a more accurate and elegant explanation for celestial mechanics. Its simplicity, predictive accuracy, and ability to explain retrograde motion set it apart from the previously accepted geocentric model. Today, the heliocentric model remains the foundation of modern astronomy and represents our current understanding of our place in the solar system.
Astronomical Evidence
Observational Support for Heliocentrism
The heliocentric model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century was not just a theoretical concept but was supported by various observational evidence. Astronomers and scientists conducted extensive observations and measurements to validate the heliocentric model and provide evidence for the central position of the Sun in our solar system. Some of the key observational evidence include:
– Planetary motion: Observations of the planetary motions, including the apparent retrograde motion, supported the heliocentric model. The retrograde motion of planets such as Mars, where they appear to move backwards in the sky, can be explained by the relative positions and velocities of the Earth and other planets in their orbits.
– Parallax: Parallax is the apparent shift in the position of a celestial object when viewed from different points. Astronomers were able to measure the parallax of stars, which provided evidence for heliocentrism. The observed parallax confirmed the motion of Earth around the Sun and the stationary nature of the stars.
– Kepler’s Laws: Johannes Kepler, a German astronomer, provided further support for the heliocentric model with his three laws of planetary motion. These laws, derived from detailed observations of planetary positions and motions, established the elliptical nature of planetary orbits around the Sun. Kepler’s laws added precision to the heliocentric model and strengthened its credibility.
– Gravitational forces: Isaac Newton’s theory of gravitation, which explained the force of attraction between celestial bodies, provided a further explanation for the heliocentric model. The gravitational forces exerted by the Sun on the planets and other celestial objects helped in understanding the precise motions and interactions within the solar system.
The Demise of Geocentrism
The adoption of the heliocentric model and the subsequent accumulation of astronomical evidence eventually led to the decline of the geocentric worldview. Over time, as scientific knowledge advanced and technology improved, the flaws and limitations of the geocentric model became apparent. Here are some of the reasons why geocentrism was eventually replaced by heliocentrism:
– Inaccurate predictions: Geocentrism struggled to accurately predict the positions and motions of celestial bodies. The complex and convoluted system of epicycles and deferents used to explain the movements of planets and stars in the geocentric model failed to match the observations and measurements made by astronomers.
– Contradictory observations: The observations of comets and the phases of Venus provided evidence against the geocentric model. Comets in highly elliptical orbits and the varying illumination of Venus during its phases were difficult to explain within the geocentric framework.
– Occultations and transits: The occurrence of occultations (when one celestial body passes in front of another) and transits (when a celestial body crosses the disc of another) also contradicted the geocentric model. These events could be observed from different locations on Earth and were inconsistent with a stationary Earth at the center of the universe.
– Alternative explanations: The heliocentric model provided a simpler, more elegant explanation for the observed motions and phenomena in the solar system. It offered a coherent framework that encompassed the various observations and provided a more accurate basis for further scientific inquiry.
In conclusion, the heliocentric model of the solar system introduced by Nicolaus Copernicus and supported by solid astronomical evidence revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics. The observations of planetary motions, parallax measurements, Kepler’s laws, and Newtonian gravity all provided empirical support for heliocentrism. The demise of the geocentric model was inevitable as its predictions failed to match observations and alternative explanations emerged. Today, the heliocentric model remains the foundation of modern astronomy and continues to shape our understanding of the universe.
Observations Supporting Heliocentrism
Astronomical Evidence
Observational Support for Heliocentrism
The heliocentric model, proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century, received significant support from a wealth of observational evidence. Astronomers and scientists conducted extensive observations and measurements, providing validation for the heliocentric model and solidifying the central position of the Sun in our solar system. Several key pieces of observational evidence include:
– Planetary motion: The observation of planetary motion, including the apparent retrograde motion, offered support for the heliocentric model. The retrograde motion, in which planets like Mars appear to move backwards, could be explained by the relative positions and velocities of Earth and other planets in their orbits.
– Parallax: Astronomers were able to measure the parallax of stars, providing evidence that confirmed heliocentrism. The observed parallax affirmed the motion of Earth around the Sun and the stationary nature of the stars.
– Kepler’s Laws: Johannes Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion, derived from detailed observations, further supported the heliocentric model. These laws established the elliptical nature of planetary orbits around the Sun, enhancing the precision and credibility of the heliocentric model.
– Gravitational forces: Isaac Newton’s theory of gravitation, explaining the attraction between celestial bodies, provided an additional explanation for the heliocentric model. Understanding the gravitational forces exerted by the Sun on planets and other celestial objects allowed for a more precise understanding of motions and interactions within the solar system.
The Transition from Geocentrism
The acceptance of the heliocentric model and the accumulation of astronomical evidence eventually led to the demise of the geocentric worldview. As scientific knowledge advanced and technology improved, the limitations and flaws of the geocentric model became increasingly apparent. Here are some reasons why heliocentrism eventually replaced geocentrism:
– Inaccurate predictions: Geocentrism struggled to accurately predict the positions and motions of celestial bodies. The convoluted system of epicycles and deferents used to explain movements within the geocentric model failed to align with the observations made by astronomers.
– Contradictory observations: The observation of comets and the phases of Venus provided evidence against the geocentric model. Comets with highly elliptical orbits and the varying illumination of Venus during its phases were challenging to reconcile within the geocentric framework.
– Occultations and transits: Occultations, when one celestial body passes in front of another, and transits, when a celestial body crosses the disc of another, contradicted the geocentric model. The ability to observe these events from different locations on Earth was inconsistent with the geocentric assumption of a stationary Earth at the center of the universe.
– Alternative explanations: The heliocentric model offered a simpler, more elegant explanation for observed motions and phenomena in the solar system. It provided a coherent framework that encompassed various observations and formed a more accurate basis for further scientific inquiry.
In conclusion, the heliocentric model of the solar system, introduced by Nicolaus Copernicus and bolstered by a wealth of astronomical evidence, revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics. Observational support for heliocentrism, including planetary motion, parallax measurements, Kepler’s laws, and Newtonian gravity, provided empirical evidence for this model. The decline of the geocentric model was inevitable as its predictions failed to match observations and alternative explanations emerged. Today, the heliocentric model remains the foundation of modern astronomy, shaping our comprehension of the universe.
Scientific Experiments and Data
Experimental Support for Heliocentrism
The heliocentric model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century was not just a theoretical concept, but it was also backed by scientific experiments and data that supported the central position of the Sun in our solar system. Through meticulous observations and measurements, astronomers and scientists were able to validate the heliocentric model and gather evidence in its favor. Some of the key scientific experiments and data include:
– Astronomical observations: Scientists made detailed observations of planetary motion, including the apparent retrograde motion, which supported the heliocentric model. The study of these motions, particularly the retrograde motion of planets like Mars, revealed the relative positions and velocities of the Earth and other planets in their respective orbits.
– Visual and telescopic observations: Scientists used both visual observations and the newly invented telescope to gather evidence for heliocentrism. Visual observations of celestial objects allowed for the measurement of parallax, the apparent shift in an object’s position when viewed from different angles. This measurement provided confirmation of Earth’s motion around the Sun and the fixed nature of the stars. Telescopic observations provided even more precise data on the positions and motions of planets, further supporting the heliocentric model.
– Kepler’s laws and orbital data: Johannes Kepler’s laws of planetary motion played a crucial role in reinforcing the heliocentric model. Derived from extensive observations, Kepler’s laws established that planets move in elliptical orbits around the Sun, providing quantitative and precise data that supported the heliocentric model.
– Gravitational effects: Isaac Newton’s theory of gravitation, formulated later, explained the gravitational forces between celestial bodies. This theory provided a comprehensive explanation for the heliocentric model, as the gravitational forces exerted by the Sun on the planets and other objects accounted for their precise motions and interactions within the solar system.
The Shift from Geocentrism to Heliocentrism
The adoption of the heliocentric model and the accumulation of scientific experiments and data gradually led to the replacement of the geocentric worldview. As scientific knowledge advanced and technology improved, the flaws and limitations of the geocentric model became more evident. Here are some of the reasons why geocentrism was eventually superseded by heliocentrism:
– Lack of accurate predictions: The geocentric model struggled to accurately predict the positions and motions of celestial bodies. The intricate system of epicycles and deferents used in the geocentric model failed to align with the observations and measurements made by astronomers.
– Inconsistent observations: Observations of comets and the phases of Venus presented evidence against the geocentric model. The highly elliptical orbits of comets and the varying illumination observed during the phases of Venus were not easily explained within the geocentric framework.
– Occultations and transits: The occurrence of occultations (when one celestial body passes in front of another) and transits (when a celestial body crosses the disc of another) contradicted the geocentric model. These events could be witnessed from different locations on Earth and were inconsistent with the notion of a stationary Earth at the center of the universe.
– Simplicity and coherence of the heliocentric model: The heliocentric model offered a simpler and more elegant explanation for observed motions and phenomena in the solar system. It provided a comprehensive framework that encompassed various observations and served as a basis for further scientific inquiry.
In conclusion, the heliocentric model of the solar system, supported by scientific experiments and data, revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics. Astronomical observations, telescopic measurements, Kepler’s laws, and Newton’s theory of gravitation all contributed to the empirical support for heliocentrism. Over time, the geocentric model became increasingly untenable as it failed to align with observations and alternative explanations emerged. Today, the heliocentric model remains the foundation of modern astronomy, continually enhancing our comprehension of the universe.
Opposition and Controversies
Opposition from the Church
The adoption of the heliocentric model faced significant opposition from the Church, particularly the Roman Catholic Church, during the 16th and 17th centuries. This opposition stemmed from a combination of religious doctrines, theological interpretations, and concerns about the potential challenges to the Church’s authority. Some of the key factors that contributed to the Church’s opposition include:
– Geocentrism in religious texts: The belief in a stationary Earth at the center of the universe was deeply ingrained in religious texts, such as the Bible. Literal interpretations of these texts led many religious scholars and leaders to reject the heliocentric model as contradictory to their understanding of divine teachings.
– Threat to the Church’s authority: Accepting the heliocentric model meant questioning the Church’s interpretation of the universe and the role of humanity within it. This posed a threat to the established power structure of the Church, as it would undermine its claims to exclusive knowledge and authority over matters of faith and science.
– Galileo’s conflict with the Church: Galileo Galilei, one of the prominent supporters of heliocentrism, faced significant opposition and persecution from the Church. His endorsement of the heliocentric model and his publication of works that advocated for it challenged the Church’s authority and led to his trial and condemnation for heresy.
Controversies and Challenges
The shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism was not a smooth process and was marked by several controversies and challenges. These controversies were fueled by conflicting scientific and religious perspectives, as well as the limitations of available technology and information at the time. Some of the key controversies and challenges include:
– Resistance from the scientific community: Not all scientists of the time readily accepted the heliocentric model. Some prominent astronomers and scholars, such as Tycho Brahe, proposed alternative models that attempted to reconcile both geocentric and heliocentric ideas.
– Confirmation bias: Confirmation bias, the tendency to interpret or seek out evidence that supports one’s existing beliefs, also played a role in hindering the acceptance of heliocentrism. Scientists and scholars who were invested in the geocentric model often focused on finding evidence that supported their views, rather than objectively evaluating the available empirical data.
– Technological limitations: The lack of advanced telescopes and observational tools posed challenges in gathering precise and accurate data to support the heliocentric model. The limitations in available technology hindered the ability to fully comprehend the complexities of celestial motion and contributed to the controversies surrounding the heliocentric model.
– Religious implications: The eventual acceptance of heliocentrism forced religious institutions to reinterpret their theological doctrines and adapt to the new scientific understanding. This process was often met with resistance and debates within religious circles as they grappled with the implications of these changes on their belief systems.
In summary, the adoption of the heliocentric model faced significant opposition from the Church and was marked by controversies and challenges. The Church’s opposition was rooted in religious doctrines and concerns about authority, particularly in relation to their interpretation of religious texts. Additionally, the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism was not a seamless process and faced resistance from both the scientific community and technological limitations of the time. These controversies and challenges highlight the social, cultural, and ideological factors that influence the acceptance and advancement of scientific ideas.
Religious and Philosophical Opposition
Challenges from Religious Beliefs
The shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism faced significant opposition from religious beliefs and doctrines prevalent at the time. Certain religious organizations and individuals interpreted religious texts, particularly those in the Judeo-Christian tradition, as supporting the geocentric worldview. This created tension between scientific observations and interpretations of religious scriptures. Some key challenges from religious beliefs include:
– Literal interpretation of religious texts: Some religious groups and individuals adhered to a literal interpretation of religious texts, assuming that they provided an accurate account of the physical world. Certain passages were interpreted as affirming the geocentric model, leading to conflicting views between religious teachings and scientific evidence.
– Scriptural authority: In a time when religious authority held great influence, proponents of geocentrism argued that deviating from the accepted interpretation of religious texts would undermine religious authority and principles. The concept of Earth being a fixed and central point in the universe held theological significance for some, and any challenge to this belief was seen as a threat.
Philosophical and Ethical Considerations
In addition to religious opposition, the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism also encountered philosophical and ethical considerations that influenced the reception and acceptance of the heliocentric model. Some of the key factors include:
– Anthropocentric view of the universe: The geocentric model, with Earth at the center, reinforced the idea of humanity’s central position in the universe. This anthropocentric view of the world was deeply ingrained in philosophical and ethical traditions, making the acceptance of heliocentrism challenging for some who perceived it as diminishing human importance.
– Social and political implications: The acceptance of new scientific ideas can have far-reaching social and political consequences. The geocentric model was deeply ingrained in societal structures and power hierarchies, particularly in relation to religious authority. The challenging of geocentrism and the acceptance of heliocentrism necessitated a significant shift in worldview, which inherently posed challenges to existing power structures.
– Resistance to change: The human tendency to resist change, particularly when it challenges deeply held beliefs and societal norms, also influenced the opposition to heliocentrism. The adoption of heliocentrism required individuals and societies to reconsider their understanding of the universe and confront the discomfort that comes with paradigm shifts.
Despite these challenges, the empirical evidence supporting the heliocentric model gradually gained acceptance and prevailed over religious and philosophical opposition. Over time, scientific progress and advancements in understanding led to a reconciliation between scientific explanations and religious doctrines, demonstrating that these two realms of knowledge can coexist.
It is important to note that this blog section aims to highlight the opposition faced by the heliocentric model and does not intend to undermine the religious or philosophical perspectives. The purpose is to provide a contextual understanding of the challenges encountered during the transition from geocentrism to heliocentrism, ensuring a holistic view of the historical developments in scientific thought and their social and cultural implications.
The Copernican Revolution and its Impact
Challenges from Religious Beliefs
The shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism faced significant opposition from religious beliefs and doctrines prevalent at the time. Certain religious organizations and individuals interpreted religious texts, particularly those in the Judeo-Christian tradition, as supporting the geocentric worldview. This created tension between scientific observations and interpretations of religious scriptures. Some key challenges from religious beliefs include:
– Literal interpretation of religious texts: Some religious groups and individuals adhered to a literal interpretation of religious texts, assuming that they provided an accurate account of the physical world. Certain passages were interpreted as affirming the geocentric model, leading to conflicting views between religious teachings and scientific evidence.
– Scriptural authority: In a time when religious authority held great influence, proponents of geocentrism argued that deviating from the accepted interpretation of religious texts would undermine religious authority and principles. The concept of Earth being a fixed and central point in the universe held theological significance for some, and any challenge to this belief was seen as a threat.
Philosophical and Ethical Considerations
In addition to religious opposition, the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism also encountered philosophical and ethical considerations that influenced the reception and acceptance of the heliocentric model. Some of the key factors include:
– Anthropocentric view of the universe: The geocentric model, with Earth at the center, reinforced the idea of humanity’s central position in the universe. This anthropocentric view of the world was deeply ingrained in philosophical and ethical traditions, making the acceptance of heliocentrism challenging for some who perceived it as diminishing human importance.
– Social and political implications: The acceptance of new scientific ideas can have far-reaching social and political consequences. The geocentric model was deeply ingrained in societal structures and power hierarchies, particularly in relation to religious authority. The challenging of geocentrism and the acceptance of heliocentrism necessitated a significant shift in worldview, which inherently posed challenges to existing power structures.
– Resistance to change: The human tendency to resist change, particularly when it challenges deeply held beliefs and societal norms, also influenced the opposition to heliocentrism. The adoption of heliocentrism required individuals and societies to reconsider their understanding of the universe and confront the discomfort that comes with paradigm shifts.
Despite these challenges, the empirical evidence supporting the heliocentric model gradually gained acceptance and prevailed over religious and philosophical opposition. Over time, scientific progress and advancements in understanding led to a reconciliation between scientific explanations and religious doctrines, demonstrating that these two realms of knowledge can coexist.
It is important to note that this section aims to highlight the opposition faced by the heliocentric model and does not intend to undermine the religious or philosophical perspectives. The purpose is to provide a contextual understanding of the challenges encountered during the transition from geocentrism to heliocentrism, ensuring a holistic view of the historical developments in scientific thought and their social and cultural implications.
Impact and Legacy
Scientific Progress
The acceptance of the heliocentric model marked a significant milestone in the advancement of scientific understanding. By challenging the prevailing geocentric view and providing empirical evidence for the motion of celestial bodies, astronomers paved the way for a more accurate comprehension of the universe. This breakthrough laid the foundation for future scientific discoveries and theories in the field of astronomy and physics.
Advancements in Technology
The shift to the heliocentric model also spurred advancements in observational and technological capabilities. Astronomers developed more sophisticated instruments, such as telescopes and sextants, to better observe and measure celestial objects. These innovations not only enhanced our understanding of the solar system but also set the stage for the development of modern astronomy and space exploration.
Reconciliation of Science and Religion
Over time, the acceptance of the heliocentric model contributed to the reconciliation of science and religion. As scientific knowledge expanded, religious institutions and thinkers began to interpret religious texts in a metaphorical or symbolic way, allowing for a harmony between scientific explanations and religious beliefs. This recognition that science and religion can coexist without contradicting each other has had a profound impact on the relationship between these two realms of human understanding.
Shift in Worldview
The adoption of the heliocentric model brought about a fundamental shift in human worldview. It challenged the notion of Earth as the center of the universe and placed humanity in a more humble and interconnected position within the cosmos. This shift not only affected scientific thought but also influenced broader philosophical, ethical, and cultural perspectives. It paved the way for new ways of thinking about our place in the universe and our responsibility towards the natural world.
Legacy of Exploration and Discovery
The acceptance of the heliocentric model opened up new horizons for exploration and discovery. It inspired scientists and explorers to seek a deeper understanding of the universe and led to breakthroughs in fields beyond astronomy, including physics, mathematics, and cosmology. The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in our modern space exploration programs, our understanding of celestial mechanics, and the technological advancements that have arisen as a result.
In conclusion, the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism had far-reaching consequences on scientific progress, technological advancements, the reconciliation of science and religion, human worldview, and the legacy of exploration. Despite the religious and philosophical opposition faced, the overwhelming evidence in support of the heliocentric model prevailed, empowering mankind to uncover the mysteries of the universe and reshape our understanding of our place in it. This significant scientific revolution continues to shape our society and our quest for knowledge about the cosmos.
Influence on Scientific Thought
Revolutionizing Astronomy
The acceptance of the heliocentric model revolutionized the field of astronomy. Astronomers were now able to accurately describe the motion of celestial bodies, leading to a more precise understanding of the universe. This breakthrough paved the way for future scientific discoveries and theories in astronomy and physics, propelling scientific progress forward.
Technical Advancements
The shift to the heliocentric model also prompted advancements in observational and technological capabilities. Astronomers developed more advanced instruments, such as telescopes and sextants, to observe and measure celestial objects with greater accuracy. These innovations not only enhanced our understanding of the solar system but also laid the foundation for the development of modern astronomy and space exploration.
Integration of Science and Religion
Over time, the acceptance of the heliocentric model facilitated the integration of science and religion. Religious institutions and thinkers began to interpret religious texts metaphorically, allowing for a harmonious coexistence of scientific explanations and religious beliefs. This recognition that science and religion can complement each other instead of contradicting has had a profound impact on the relationship between these two realms of human understanding.
Paradigm Shift in Worldview
The adoption of the heliocentric model brought about a paradigm shift in the human worldview. It challenged the long-held belief that Earth was the center of the universe and instead placed humanity in a more humble and interconnected position within the cosmos. This shift not only influenced scientific thought but also had broader implications for philosophy, ethics, and culture, reshaping our perspectives on our place in the universe and our responsibility towards the natural world.
Legacy of Exploration and Discovery
The acceptance of the heliocentric model opened up new doors for exploration and discovery. It inspired scientists and explorers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the universe, leading to breakthroughs in numerous fields, including physics, mathematics, and cosmology. The legacy of the heliocentric model can be observed in our modern-day space exploration programs, our understanding of celestial mechanics, and the technological advancements that have emerged as a result.
In conclusion, the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism had a profound impact on scientific thought, technological advancements, the integration of science and religion, the human worldview, and the legacy of exploration. Despite facing opposition from religious and philosophical circles, the overwhelming evidence supporting the heliocentric model prevailed, enabling humanity to uncover the secrets of the universe and reshape our understanding of our place in it. This significant scientific revolution continues to shape society and our pursuit of knowledge about the cosmos.
Modern Understanding of the Solar System
Scientific Progress
The acceptance of the heliocentric model marked a significant milestone in the advancement of scientific understanding. The shift from the geocentric view to the heliocentric model revolutionized our understanding of the solar system. By challenging the prevailing belief that Earth was the center of the universe, astronomers paved the way for a more accurate comprehension of the cosmos. This breakthrough laid the foundation for future scientific discoveries and theories in the field of astronomy and physics.
Advancements in Technology
The shift to the heliocentric model also spurred advancements in observational and technological capabilities. Astronomers developed more sophisticated instruments, such as telescopes and sextants, to better observe and measure celestial objects. These innovations not only enhanced our understanding of the solar system but also set the stage for the development of modern astronomy and space exploration.
Reconciliation of Science and Religion
Over time, the acceptance of the heliocentric model contributed to the reconciliation of science and religion. As scientific knowledge expanded, religious institutions and thinkers began to interpret religious texts in a metaphorical or symbolic way, allowing for a harmony between scientific explanations and religious beliefs. This recognition that science and religion can coexist without contradicting each other has had a profound impact on the relationship between these two realms of human understanding.
Shift in Worldview
The adoption of the heliocentric model brought about a fundamental shift in human worldview. It challenged the notion of Earth as the center of the universe and placed humanity in a more humble and interconnected position within the cosmos. This shift not only affected scientific thought but also influenced broader philosophical, ethical, and cultural perspectives. It paved the way for new ways of thinking about our place in the universe and our responsibility towards the natural world.
Legacy of Exploration and Discovery
The acceptance of the heliocentric model opened up new horizons for exploration and discovery. It inspired scientists and explorers to seek a deeper understanding of the universe and led to breakthroughs in fields beyond astronomy, including physics, mathematics, and cosmology. The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in our modern space exploration programs, our understanding of celestial mechanics, and the technological advancements that have arisen as a result.
In conclusion, the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism had far-reaching consequences on scientific progress, technological advancements, the reconciliation of science and religion, and human worldview. The acceptance and adoption of the heliocentric model revolutionized our understanding of the solar system and paved the way for further exploration and discovery. Today, our modern understanding of the solar system is built upon the foundations laid by astronomers who challenged the prevailing geocentric view. This significant scientific revolution continues to shape our society and our quest for knowledge about the cosmos.
Heliocentrism vs. Geocentrism
The Shift in Scientific Understanding
The acceptance of the heliocentric model over the geocentric view marked a significant milestone in the advancement of scientific understanding. Astronomers challenged the prevailing belief that Earth was the center of the universe, leading to a revolution in our comprehension of the solar system. This breakthrough laid the foundation for future scientific discoveries and theories in the field of astronomy and physics.
Advancements in Observational Technology
The shift to the heliocentric model also spurred advancements in observational and technological capabilities. Astronomers developed more sophisticated instruments, such as telescopes and sextants, to better observe and measure celestial objects. These innovations not only enhanced our understanding of the solar system but also set the stage for the development of modern astronomy and space exploration.
A Reconciliation of Science and Religion
Over time, the acceptance of the heliocentric model contributed to the reconciliation of science and religion. As scientific knowledge expanded, religious institutions and thinkers began to interpret religious texts in a metaphorical or symbolic way, allowing for a harmony between scientific explanations and religious beliefs. This recognition that science and religion can coexist without contradicting each other has had a profound impact on the relationship between these two realms of human understanding.
A Paradigm Shift in Worldview
The adoption of the heliocentric model brought about a fundamental shift in human worldview. It challenged the notion of Earth as the center of the universe and placed humanity in a more humble and interconnected position within the cosmos. This shift not only affected scientific thought but also influenced broader philosophical, ethical, and cultural perspectives. It paved the way for new ways of thinking about our place in the universe and our responsibility towards the natural world.
The Legacy of the Heliocentric Model
The acceptance of the heliocentric model opened up new horizons for exploration and discovery. It inspired scientists and explorers to seek a deeper understanding of the universe, leading to breakthroughs in fields beyond astronomy, including physics, mathematics, and cosmology. Today, our modern understanding of the solar system is built upon the foundations laid by astronomers who challenged the prevailing geocentric view. The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in our modern space exploration programs, our understanding of celestial mechanics, and the technological advancements that have arisen as a result.
In conclusion, the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism had far-reaching consequences on scientific progress, technological advancements, the reconciliation of science and religion, and human worldview. The acceptance and adoption of the heliocentric model revolutionized our understanding of the solar system and paved the way for further exploration and discovery. This significant scientific revolution continues to shape our society and our quest for knowledge about the cosmos.
A Comparison of Heliocentric and Geocentric Models
Scientific Progress
The acceptance of the heliocentric model marked a significant milestone in the advancement of scientific understanding. Astronomers challenging the prevailing geocentric view revolutionized our understanding of the solar system, paving the way for future scientific discoveries and theories in the field of astronomy and physics.
Advancements in Technology
The shift to the heliocentric model spurred advancements in observational and technological capabilities. Astronomers developed sophisticated instruments, such as telescopes and sextants, to better observe and measure celestial objects. These innovations not only enhanced our understanding of the solar system but also set the stage for the development of modern astronomy and space exploration.
Reconciliation of Science and Religion
Over time, the acceptance of the heliocentric model contributed to the reconciliation of science and religion. As scientific knowledge expanded, religious institutions and thinkers began to interpret religious texts in a metaphorical or symbolic way, allowing for a harmony between scientific explanations and religious beliefs. This recognition that science and religion can coexist without contradicting each other has had a profound impact on the relationship between these two realms of human understanding.
Shift in Worldview
The adoption of the heliocentric model brought about a fundamental shift in human worldview. It challenged the notion of Earth as the center of the universe and placed humanity in a more humble and interconnected position within the cosmos. This shift not only affected scientific thought but also influenced broader philosophical, ethical, and cultural perspectives. It paved the way for new ways of thinking about our place in the universe and our responsibility towards the natural world.
Legacy of Exploration and Discovery
The acceptance of the heliocentric model opened up new horizons for exploration and discovery. It inspired scientists and explorers to seek a deeper understanding of the universe and led to breakthroughs in fields beyond astronomy, including physics, mathematics, and cosmology. The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in our modern space exploration programs, our understanding of celestial mechanics, and the technological advancements that have arisen as a result.
In conclusion, the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism had far-reaching consequences on scientific progress, technological advancements, the reconciliation of science and religion, and human worldview. The acceptance and adoption of the heliocentric model revolutionized our understanding of the solar system and paved the way for further exploration and discovery. Today, our modern understanding of the solar system is built upon the foundations laid by astronomers who challenged the prevailing geocentric view. This significant scientific revolution continues to shape our society and our quest for knowledge about the cosmos.
Misconceptions and Myths
Resistance to Change
One common misconception about the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism is that it was readily accepted by all. In reality, there was significant resistance from religious authorities and conservative thinkers who viewed the heliocentric model as contradicting religious teachings and undermining the authority of the Church. Many prominent figures, such as Galileo Galilei, faced persecution and censorship for promoting the heliocentric view.
Flat Earth Myth
Another misconception is the belief that before the acceptance of the heliocentric model, people believed that the Earth was flat. This notion is incorrect. Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks, Egyptians, and Chinese, had already deduced that the Earth was spherical based on various observations and logical reasoning. The shift to heliocentrism did not change the understanding of Earth’s shape but rather its position in the universe.
Copernican Revolution
It is also important to clarify the term “Copernican Revolution,” often used to describe the shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism. While Nicolaus Copernicus’ work was a significant contribution to the development and popularization of the heliocentric model, it was not solely responsible for the shift. Other astronomers, such as Aristarchus of Samos, had proposed similar ideas centuries earlier. The acceptance of heliocentrism was a gradual process that involved multiple individuals and accumulated evidence over time.
Disregard for Observational Evidence
Contrary to popular belief, the choice to believe in geocentrism was not solely based on religious dogma. Some proponents of geocentrism, such as Claudius Ptolemy, developed sophisticated models that accurately predicted the positions of celestial objects. These models were based on the available observational evidence and mathematical calculations at the time. It was not until astronomers challenged these models and presented compelling evidence for heliocentrism that the prevailing view started to shift.
Non-Revolutionary Implications
While the adoption of the heliocentric model had profound implications for science and human worldview, it is important to note that it did not completely overturn all existing knowledge and beliefs about the universe. The heliocentric model was not an entirely accurate representation of the solar system, as later advancements in physics and cosmology revealed. It was a significant step forward in understanding our place in the universe but still required refinement and further discoveries.
In summary, the transition from geocentrism to heliocentrism was not without its challenges and misconceptions. While some resisted the change due to religious and societal reasons, others embraced the new understanding of the solar system. It is essential to address these misconceptions and myths surrounding the shift to heliocentrism to ensure an accurate understanding of the scientific progress and implications of this monumental paradigm shift.
Heliocentric Theory Today
Continued Scientific Advancements
The acceptance and adoption of the heliocentric model have continued to drive scientific advancements in our understanding of the solar system and the broader universe. Through ongoing research, astronomers have discovered exoplanets orbiting other stars, further confirming the principles of the heliocentric model. Scientists have also been able to refine our knowledge of the sun’s behavior and the gravitational interactions within the solar system, leading to a deeper understanding of celestial mechanics.
Technological Innovations
The shift to the heliocentric model has also spurred the development of new technologies that have revolutionized astronomical observations. Modern telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, provide a level of detail and clarity in observing distant celestial objects that was unimaginable in the past. These tools enable scientists to study the formation of galaxies, the behavior of distant stars, and the exploration of other planetary systems.
Interdisciplinary Connections
The adoption of the heliocentric model has had a profound impact not only within the field of astronomy but also in other scientific disciplines. The principles of heliocentrism are fundamental to our understanding of physics, as they form the basis of Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation. The heliocentric model also plays a crucial role in the study of cosmology, providing the framework for the Big Bang theory and our understanding of the origin and evolution of the universe.
Integration of Science and Religion
In modern times, the acceptance of the heliocentric model has resulted in greater integration and harmony between scientific knowledge and religious beliefs. Many religious traditions have embraced scientific explanations of the natural world, recognizing that they complement rather than contradict theological teachings. This recognition allows for a more nuanced understanding of both science and religion and encourages respectful dialogue between the two realms.
Impacts on Society and Culture
The shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism continues to influence broader philosophical, ethical, and cultural perspectives. The realization that Earth is but one small planet among countless others has instilled a sense of humility and interconnectedness within humanity. This perspective has prompted discussions around environmentalism and sustainability, as it highlights the importance of stewardship and responsibility towards our planet and the wider cosmos.
Ongoing Exploration and Discovery
The legacy of the heliocentric model can also be seen in ongoing exploration and discovery in the realm of space. Missions from various space agencies continue to study our solar system, investigating the geology and atmospheres of planets and moons. Additionally, research efforts focus on the search for life beyond Earth, utilizing the principles of heliocentrism to guide the exploration for habitable environments within our galaxy.
In summary, the heliocentric model has had a lasting impact on scientific progress, technological advancements, interdisciplinary connections, and our understanding of the relationship between science and religion. It continues to inspire new discoveries and shape our worldview, guiding our exploration of the solar system and the broader universe. Through ongoing research and technological innovations, heliocentrism remains a foundational principle in modern astronomy and our quest for knowledge about the cosmos.
A Confirmation and Acceptance
Continued Scientific Advancements
The heliocentric model of the solar system, after facing initial skepticism and resistance, has gained widespread acceptance among the scientific community. This theory, proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century, suggests that the Earth and other planets orbit the Sun. Over the years, numerous scientific advancements have further confirmed and expanded our understanding of this model.
Advancements in Astronomical Research
Through ongoing research, astronomers have made significant discoveries that validate the principles of the heliocentric model. The detection of exoplanets, planets that orbit stars outside our solar system, provides compelling evidence of the universality of the heliocentric concept. By studying the behavior of these exoplanets, scientists have gained insights into the diversity and formation of planetary systems throughout the galaxy.
Refinement of Solar Knowledge
The heliocentric model has also led to a better understanding of the Sun, the central body of our solar system. Through careful observations and analysis, scientists have been able to study the Sun’s behavior, including its magnetic activity, solar flares, and sunspots. This improved understanding of the Sun’s dynamics has practical applications, such as predicting space weather and its potential impact on Earth’s technological infrastructure.
Deeper Understanding of Celestial Mechanics
The heliocentric model has been instrumental in advancing our knowledge of celestial mechanics, especially the gravitational interactions within the solar system. This understanding has allowed scientists to accurately predict the movements of planets, moons, and other celestial bodies. The application of Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation, which are based on the heliocentric model, has proven to be invaluable in space exploration missions and satellite positioning systems.
Technological Innovations in Astronomy
The acceptance of the heliocentric model has driven the development of innovative technologies that have revolutionized astronomical observations. Modern telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, provide unprecedented levels of clarity and detail in studying distant celestial objects. These advancements have enabled scientists to explore the formation and evolution of galaxies, the behavior of distant stars, and the potential for life on exoplanets.
Interdisciplinary Applications
The heliocentric model’s impact extends beyond astronomy to other scientific disciplines. It forms the foundation of our understanding of physics, particularly as it relates to Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation. The principles of heliocentrism have also shaped the field of cosmology, providing the framework for the Big Bang theory and our understanding of the origins and evolution of the universe.
Integration of Science and Religion
The acceptance of the heliocentric model has brought about a greater harmony between scientific knowledge and religious beliefs. Many religious traditions have recognized that scientific explanations of the natural world complement theological teachings rather than contradict them. This integration allows for a more nuanced understanding of both science and religion and encourages respectful dialogue between the two realms.
Influence on Society and Culture
The transition from geocentrism to heliocentrism has had significant implications for society and culture. The realization that Earth is just one small planet among many has fostered a sense of humility and interconnectivity among humanity. This perspective has influenced discussions on environmentalism and sustainability, emphasizing the importance of responsible stewardship towards our planet and the broader cosmos.
Continued Exploration and Discoveries
The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in ongoing space exploration and discovery efforts. Missions launched by various space agencies continue to uncover new knowledge about our solar system, including the geology and atmospheres of planets and moons. The principles of heliocentrism guide the search for habitable environments and the exploration for extraterrestrial life within our galaxy and beyond.
In summary, the acceptance of the heliocentric model has propelled scientific advancements, technological innovations, interdisciplinary connections, and a deeper understanding of the relationship between science and religion. This model continues to inspire new discoveries and shape our worldview, guiding our exploration of the solar system and the broader universe. With ongoing research and technological innovations, heliocentrism remains a foundational principle in modern astronomy and humanity’s quest for knowledge about the cosmos.
Further Discoveries and Developments
Continued Scientific Advancements
The acceptance and adoption of the heliocentric model have continued to drive scientific advancements in our understanding of the solar system and the broader universe. Ongoing research has led to the discovery of exoplanets orbiting other stars, providing further evidence for the principles of the heliocentric model. Astronomers have also made significant progress in refining our knowledge of the sun’s behavior and the gravitational interactions within the solar system. This deeper understanding of celestial mechanics has paved the way for more accurate predictions and models.
Technological Innovations
The shift to the heliocentric model has spurred the development of advanced technologies that have revolutionized astronomical observations. Modern telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, provide unprecedented detail and clarity in observing distant celestial objects. These tools have enabled scientists to study the formation of galaxies, the behavior of distant stars, and the exploration of other planetary systems. Additionally, advancements in computer technology and data analysis have allowed for more sophisticated modeling and simulations of the solar system and beyond.
Interdisciplinary Connections
The adoption of the heliocentric model has not only advanced our understanding of astronomy but also interconnected various scientific disciplines. The principles of heliocentrism form the basis of Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation, fundamental to our understanding of physics. Furthermore, the heliocentric model plays a crucial role in the study of cosmology, providing the framework for the Big Bang theory and our understanding of the origin and evolution of the universe. This integration of scientific knowledge across disciplines has led to a more comprehensive understanding of the natural world.
Integration of Science and Religion
Acceptance of the heliocentric model has resulted in greater integration and harmony between scientific knowledge and religious beliefs. Many religious traditions have embraced scientific explanations of the natural world, recognizing that they complement rather than contradict theological teachings. This recognition allows for a more nuanced understanding of both science and religion and promotes respectful dialogue between the two realms. It fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexity and wonder of the universe, bridging the gap between faith and scientific inquiry.
Impacts on Society and Culture
The shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism continues to influence broader philosophical, ethical, and cultural perspectives. Realizing that Earth is one among countless planets has instilled a sense of humility and interconnectedness within humanity. This perspective has spurred discussions around environmentalism and sustainability, emphasizing the importance of responsible stewardship towards our planet and the wider cosmos. The heliocentric model has also inspired art, literature, and music, shaping our cultural expressions and evoking a sense of wonder and awe towards the vastness of the universe.
Ongoing Exploration and Discovery
The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in ongoing exploration and discovery in space. Missions from various space agencies are continuously studying our solar system, investigating the geology and atmospheres of planets and moons. Efforts are also focused on the search for life beyond Earth, utilizing the principles of heliocentrism to guide the exploration for habitable environments within our galaxy. These missions and discoveries not only expand our scientific knowledge but also fuel our curiosity and imagination about the possibilities that lie beyond our own planet.
In summary, the heliocentric model has had a lasting impact on scientific progress, technological advancements, interdisciplinary connections, and the integration of science and religion. It continues to inspire new discoveries, shape our worldview, and guide our exploration of the solar system and the broader universe. Through ongoing research, technological innovations, and interdisciplinary collaboration, heliocentrism remains a fundamental principle in modern astronomy, driving our quest for knowledge and understanding of the cosmos.
Conclusion
Continued Impact on Scientific Advancements
The adoption of the heliocentric model has had a significant and lasting impact on scientific progress. Ongoing research and discoveries, such as the detection of exoplanets and advancements in our understanding of the sun’s behavior, have further reinforced the principles of heliocentrism. This deeper understanding of celestial mechanics has paved the way for more accurate predictions and models, driving advancements in our understanding of the solar system and the broader universe.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
The shift to the heliocentric model has also spurred technological innovations and advancements in the field of astronomy. Modern telescopes, including the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, have revolutionized astronomical observations by providing unprecedented detail and clarity in studying distant celestial objects. Advancements in computer technology and data analysis have also allowed for more sophisticated modeling and simulations, enhancing our understanding of the solar system and beyond.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration and Integration
The adoption of the heliocentric model has fostered greater collaboration and integration among different scientific disciplines. The principles of heliocentrism form the foundation of laws of motion and gravitation, which are fundamental to our understanding of physics. Additionally, the heliocentric model has played a vital role in the study of cosmology and the origin and evolution of the universe. This integration of scientific knowledge has led to a more comprehensive understanding of the natural world and expanded our knowledge across disciplines.
Reconciliation of Science and Religion
Acceptance of the heliocentric model has resulted in a greater reconciliation of scientific knowledge and religious beliefs. Many religious traditions have embraced scientific explanations of the natural world and recognized that they can complement theological teachings. This recognition allows for a more nuanced understanding of both science and religion and promotes respectful dialogue between the two realms. It fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexity and wonders of the universe, bridging the gap between faith and scientific inquiry.
Social and Cultural Impacts
The shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism has also had significant impacts on society and culture. Understanding that Earth is just one among countless planets has instilled a sense of humility and interconnectedness within humanity. This perspective has fueled discussions around environmentalism and sustainability, emphasizing the importance of responsible stewardship towards our planet and the wider cosmos. The heliocentric model has also inspired artistic expressions in various forms, shaping our cultural understanding and appreciation of the vastness of the universe.
Ongoing Exploration and Discovery
The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in ongoing exploration and discoveries in space. Missions from different space agencies are continuously studying our solar system, examining the geology and atmospheres of planets and moons. Efforts are also focused on the search for life beyond Earth, guided by the principles of heliocentrism in the exploration for habitable environments within our galaxy. These missions and discoveries expand our scientific knowledge and fuel our curiosity and imagination about the possibilities that lie beyond our own planet.
In summary, the heliocentric model has had a long-lasting and profound impact on scientific progress, technological advancements, interdisciplinary collaborations, and the integration of science and religion. It continues to inspire new discoveries, shape our worldview, and guide our exploration of the solar system and the broader universe. Through ongoing research, technological innovations, and interdisciplinary collaboration, heliocentrism remains a fundamental principle in modern astronomy, driving our quest for knowledge and understanding of the cosmos.
a Heliocentrism’s Contribution to Astronomy
Further Discoveries and Developments
Continued Scientific Advancements
Scientific advancements in our understanding of the solar system and the broader universe have been driven by the acceptance and adoption of the heliocentric model. Ongoing research has led to the discovery of exoplanets orbiting other stars, providing further evidence for the principles of the heliocentric model. Additionally, astronomers have made significant progress in refining our knowledge of the sun’s behavior and the gravitational interactions within the solar system. This deeper understanding of celestial mechanics has paved the way for more accurate predictions and models.
Technological Innovations
The shift to the heliocentric model has spurred the development of advanced technologies that have revolutionized astronomical observations. Modern telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, provide unprecedented detail and clarity in observing distant celestial objects. These tools have enabled scientists to study the formation of galaxies, the behavior of distant stars, and the exploration of other planetary systems. Additionally, advancements in computer technology and data analysis have allowed for more sophisticated modeling and simulations of the solar system and beyond.
Interdisciplinary Connections
The adoption of the heliocentric model has not only advanced our understanding of astronomy but also interconnected various scientific disciplines. The principles of heliocentrism form the basis of Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation, fundamental to our understanding of physics. Furthermore, the heliocentric model plays a crucial role in the study of cosmology, providing the framework for the Big Bang theory and our understanding of the origin and evolution of the universe. This integration of scientific knowledge across disciplines has led to a more comprehensive understanding of the natural world.
Integration of Science and Religion
Greater integration and harmony between scientific knowledge and religious beliefs have resulted from the acceptance of the heliocentric model. Many religious traditions have embraced scientific explanations of the natural world, recognizing that they complement rather than contradict theological teachings. This recognition allows for a more nuanced understanding of both science and religion and promotes respectful dialogue between the two realms. It fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexity and wonder of the universe, bridging the gap between faith and scientific inquiry.
Impacts on Society and Culture
The shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism continues to influence broader philosophical, ethical, and cultural perspectives. Realizing that Earth is one among countless planets has instilled a sense of humility and interconnectedness within humanity. This perspective has spurred discussions around environmentalism and sustainability, emphasizing the importance of responsible stewardship towards our planet and the wider cosmos. The heliocentric model has also inspired art, literature, and music, shaping our cultural expressions and evoking a sense of wonder and awe towards the vastness of the universe.
Ongoing Exploration and Discovery
The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in ongoing exploration and discovery in space. Missions from various space agencies are continuously studying our solar system, investigating the geology and atmospheres of planets and moons. Efforts are also focused on the search for life beyond Earth, utilizing the principles of heliocentrism to guide the exploration for habitable environments within our galaxy. These missions and discoveries not only expand our scientific knowledge but also fuel our curiosity and imagination about the possibilities that lie beyond our own planet.
In summary, the heliocentric model has had a lasting impact on scientific progress, technological advancements, interdisciplinary connections, and the integration of science and religion. It continues to inspire new discoveries, shape our worldview, and guide our exploration of the solar system and the broader universe. Through ongoing research, technological innovations, and interdisciplinary collaboration, heliocentrism remains a fundamental principle in modern astronomy, driving our quest for knowledge and understanding of the cosmos.
Continuing Relevance in Understanding the Universe
Further Scientific Discoveries and Developments
Advancements in Technology
The heliocentric model has driven the development of advanced technologies that have revolutionized astronomical observations. Modern telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, provide unprecedented detail and clarity in observing distant celestial objects. These tools have enabled scientists to study the formation of galaxies, the behavior of distant stars, and the exploration of other planetary systems. Additionally, advancements in computer technology and data analysis have allowed for more sophisticated modeling and simulations of the solar system and beyond.
Interdisciplinary Connections and Integration of Knowledge
The acceptance of the heliocentric model has not only advanced our understanding of astronomy but also interconnected various scientific disciplines. The principles of heliocentrism form the basis of Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation, fundamental to our understanding of physics. Furthermore, the heliocentric model plays a crucial role in the study of cosmology, providing the framework for the Big Bang theory and our understanding of the origin and evolution of the universe. This integration of scientific knowledge across disciplines has led to a more comprehensive understanding of the natural world.
Impacts on Society and Culture
The shift from geocentrism to heliocentrism continues to influence broader philosophical, ethical, and cultural perspectives. Realizing that Earth is one among countless planets has instilled a sense of humility and interconnectedness within humanity. This perspective has spurred discussions around environmentalism and sustainability, emphasizing the importance of responsible stewardship towards our planet and the wider cosmos. The heliocentric model has also inspired art, literature, and music, shaping our cultural expressions and evoking a sense of wonder and awe towards the vastness of the universe.
Ongoing Exploration and Discovery
The legacy of the heliocentric model can be seen in ongoing exploration and discovery in space. Missions from various space agencies are continuously studying our solar system, investigating the geology and atmospheres of planets and moons. Efforts are also focused on the search for life beyond Earth, utilizing the principles of heliocentrism to guide the exploration for habitable environments within our galaxy. These missions and discoveries not only expand our scientific knowledge but also fuel our curiosity and imagination about the possibilities that lie beyond our own planet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the heliocentric model continues to play a vital role in our understanding of the universe. It has led to further scientific discoveries, advancements in technology, and interdisciplinary connections. The acceptance of the heliocentric model has also had impacts on society and culture, shaping our worldview and inspiring new perspectives. Ongoing exploration and discovery in space are guided by the principles of heliocentrism, expanding our knowledge and fueling our curiosity. The relevance of the heliocentric model in modern astronomy underscores its significance as a fundamental principle in our quest for knowledge and understanding of the cosmos.