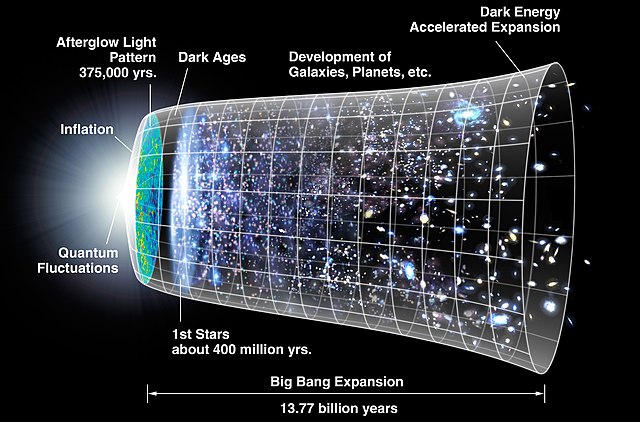
Introduction Theories on Universe’s Fate
Background information on the theories about the universe’s fate
In the field of physical cosmology, one of the fascinating topics of study is the ultimate fate of the universe. Scientists have been exploring various theoretical scenarios that could potentially explain the evolution and destiny of our universe. This exploration became possible with Albert Einstein’s 1915 theory of general relativity, which provides a framework for describing the universe on its largest scales.
Importance of understanding the ultimate fate of the universe
Understanding the ultimate fate of the universe is of great significance in the field of cosmology. It not only satisfies our curiosity about the nature of our existence but also has practical implications for the future of humanity. By comprehending how the universe may evolve, scientists can gain insights into the long-term sustainability of our planet and the potential for human colonization of other celestial bodies.
Determining the ultimate fate of the universe requires consideration of several factors:
1. Average motions of galaxies: The collective movement of galaxies plays a crucial role in determining the fate of the universe. Scientists study the distribution and dynamics of galaxies to gain insights into whether the universe will continue expanding indefinitely or if it will eventually collapse under its own gravitational pull.
2. Shape and structure of the universe: The shape and structure of the universe also influence its ultimate fate. Cosmologists consider various possibilities, such as a flat universe, a closed universe, or an open universe, each with different implications for its future evolution.
3. Amount of matter and energy in the universe: The amount of matter and energy present in the universe affects its ultimate fate as well. Factors such as dark matter and dark energy, which are still not fully understood, can significantly impact the expansion or contraction of the universe.
4. Theoretical scientific basis: The theoretical foundations provided by Einstein’s general relativity serve as the basis for exploring the ultimate fate of the universe. By applying the principles of general relativity to the universe as a whole, scientists can generate models and hypotheses about its future trajectory.
It is important to note that while scientific advancements have enabled us to speculate about the ultimate fate of the universe, precise predictions remain challenging. The vastness and complexity of the cosmos pose significant limitations on our ability to make definitive conclusions. However, ongoing research and technological advancements continue to shed light on this captivating subject, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and understanding.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the emerging scientific basis and theories surrounding the ultimate fate of the universe. Stay tuned for exciting insights into one of the most profound questions humanity has ever contemplated.
Factors Influencing the Universe’s Fate
Average motions of galaxies and their impact on the universe’s future
The average motions of galaxies play a crucial role in determining the ultimate fate of the universe. These motions can provide insights into whether the universe will continue expanding indefinitely or eventually collapse under its own gravitational pull.
The observations of galaxies moving away from each other, as discovered by Edwin Hubble in the 1920s, led to the formulation of the Big Bang theory. This theory suggests that the universe originated from a single point and has been expanding ever since. If the average motions of galaxies continue to show that they are moving apart, it indicates that the universe will likely continue expanding indefinitely.
On the other hand, if the average motions of galaxies were to reverse and show a trend of moving towards each other, it would imply that the universe’s expansion is slowing down and may eventually come to a halt. This scenario could lead to the collapse and contraction of the universe, resulting in what is known as the Big Crunch.
The shape and structure of the universe and its implications for its fate
The shape and structure of the universe also have significant implications for its ultimate fate. The geometry of the universe can be described using different mathematical models, such as flat, open, or closed.
If the universe is flat, it means that the overall geometry is parallel and will continue expanding indefinitely. In this scenario, the universe’s fate would be influenced primarily by other factors, such as the amount of matter and energy it contains.
If the universe is open or negatively curved, it suggests that the expansion will continue, but at a decreasing rate. In this case, the universe’s fate would depend on the balance between the expansion and the gravitational pull of matter and energy.
If the universe is closed or positively curved, it means that the overall geometry is curved inward. In this scenario, the expansion of the universe would eventually come to a halt and result in a contraction towards a singularity. This scenario is similar to the Big Crunch mentioned earlier.
In conclusion, several factors need to be considered in determining the universe’s origin and ultimate fate. The average motions of galaxies and the shape and structure of the universe provide valuable insights into whether the universe will continue expanding indefinitely or eventually collapse. Our understanding of these factors is based on the scientific exploration enabled by Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity. Continued research and observations are essential in unraveling the mysteries surrounding the universe’s fate.
The Amount of Matter and Energy in the Universe
Understanding the significance of matter and energy in determining the universe’s fate
The amount of matter and energy present in the universe plays a crucial role in shaping its ultimate destiny. By analyzing the composition of the universe, scientists have determined that it consists of approximately 68% dark energy, 27% dark matter, and 5% normal matter. This distribution of matter and energy is based on fitting a theoretical model to cosmological observations.
Dark energy, as its name suggests, is a mysterious form of energy that permeates throughout space and is believed to be responsible for the accelerating expansion of the universe. Its precise nature is still not fully understood, and multiple hypotheses exist to explain its origin and properties.
Dark matter, on the other hand, refers to an invisible substance that does not interact with light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. Its existence is inferred from its gravitational effects on visible matter, such as galaxies. Dark matter plays a crucial role in shaping the large-scale structure of the universe and is believed to provide the gravitational framework necessary for galaxy formation and evolution.
The presence of both dark energy and dark matter has significant implications for the fate of the universe. The exact role they play in determining the cosmic expansion and eventual destiny of the universe is still an active area of research.
Exploring the concept of dark matter and its effect on the overall destiny of the universe
Dark matter’s gravitational pull not only influences the motion of galaxies but also affects the overall structure and fate of the universe. Understanding its properties and distribution is key to unraveling the mysteries surrounding the universe’s evolution.
One possible outcome is a scenario in which the universe continues to expand indefinitely. If the average motions of galaxies continue to demonstrate a trend of moving apart, it suggests that the expansion will persist. In this case, the exact amount of dark matter and dark energy present will determine the ultimate fate of the universe. The balance between their gravitational pull and the expansion will shape whether the universe continues expanding or eventually reaches a state of maximum expansion.
Alternatively, if the average motions of galaxies were to show a reversal and indicate a trend of moving towards each other, it would suggest that the expansion is slowing down. This scenario could potentially lead to the collapse of the universe under its own gravitational pull, resulting in a contraction known as the Big Crunch. The contribution of dark matter in this scenario becomes crucial as it acts as a gravitational brake, slowing down the expansion and possibly leading to the eventual collapse.
In conclusion, the amount and distribution of matter and energy, including dark matter and dark energy, in the universe are vital in determining its fate. While dark energy drives the accelerating expansion, dark matter provides the gravitational framework necessary for the formation of galaxies. The balance between these components will shape the ultimate destiny of the universe, whether it continues expanding indefinitely or collapses under its own gravity. Continued research and observations are essential in furthering our understanding of these phenomena and unraveling the mysteries surrounding the universe’s fate.
General Relativity and the Universe’s Fate
Einstein’s theory of general relativity and its role in describing the universe on a large scale
Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity revolutionized our understanding of gravity and its effects on the fabric of space-time. This theory provides a mathematical framework for describing the universe on the largest possible scale and plays a crucial role in exploring the ultimate fate of the universe.
General relativity proposes that gravity is not simply a force between objects but instead arises from the curvature of space-time caused by mass and energy. It explains how objects with mass and energy influence the geometry of space-time, creating what we perceive as gravitational attraction.
This understanding of gravity allowed scientists to consider the universe as a whole and investigate its past, present, and future evolution. By applying general relativity, researchers can model the behavior of cosmic structures, such as galaxies, clusters, and even the entire universe.
Applying general relativity to predict and understand the fate of the universe
One of the intriguing aspects of general relativity is its ability to provide possible scenarios for the ultimate fate of the universe. By solving the equations derived from this theory, scientists can explore different outcomes and make predictions about the fate of the cosmos.
Several possible solutions to the equations of general relativity have been proposed, each implying a different fate for the universe. Some of these scenarios include:
1. Expansion Forever: If the average motions of galaxies continue to show that they are moving apart, it suggests that the universe will keep expanding indefinitely. In this case, the universe’s fate would be an eternal expansion, with galaxies drifting further apart over time.
2. Big Crunch: On the contrary, if the average motions of galaxies reverse and indicate that they are moving towards each other, it could imply a slowing down of the universe’s expansion. This scenario may lead to a contraction under the influence of gravity, resulting in a Big Crunch where the universe collapses into a singularity.
3. Eternal Static Universe: Another possibility suggested by general relativity is an eternal static universe where the expansion and contraction balance each other perfectly. In this scenario, the universe remains the same size and structure throughout its existence.
Comparative table for the different possible fates of the universe:
| Fate of the Universe | Description |
|——————|————-|
| Eternal Expansion | The universe continues to expand indefinitely with galaxies moving apart. |
| Big Crunch | The universe slows down its expansion and collapses under gravity into a singularity. |
| Eternal Static Universe | The expansion and contraction of the universe balance each other, resulting in a static state. |
In conclusion, Einstein’s theory of general relativity is instrumental in understanding the large-scale behavior of the universe and predicting its ultimate fate. By studying the average motions of galaxies, the shape and structure of the universe, and considering the solutions provided by general relativity, scientists can shed light on the mystery of our universe’s origin and destiny. Continued research and observations are vital in refining our understanding of these fundamental questions.
The Cyclic Model of the Universe
Exploring the possibility of the universe expanding and contracting in a cyclic manner
The cyclic model of the universe proposes that the universe undergoes an endless cycle of expansion and contraction, with each cycle consisting of a “big bang” followed by a “big crunch.” This theory challenges the traditional understanding of the Big Bang as a singular event that marked the beginning of the universe.
Proponents of the cyclic model argue that it provides an alternative explanation for the rapid inflation of the universe and the observed uniformity of its structure. They suggest that the universe undergoes a series of cycles, each starting with a hot and dense state similar to the Big Bang, followed by an expansion phase and eventual contraction. This cyclic nature of the universe offers a different perspective on its origins and evolution.
Examining the evidence for past cycles in the universe’s history
Scientists have been studying various pieces of observational evidence to support or refute the existence of past cycles in the history of the universe. One line of evidence comes from studying the cosmic microwave background radiation, which is considered to be remnants of the early universe. Researchers analyze the patterns and fluctuations in this radiation to understand the conditions present at different stages of the universe’s history.
Another piece of evidence comes from studying the distribution and movement of galaxies. By measuring the velocities and trajectories of galaxies, scientists can infer the dynamics of the universe and whether it is currently expanding or contracting. These measurements can provide insights into the possibility of past cycles and the potential for future ones.
However, it is essential to note that the cyclic model of the universe is still a theoretical framework, and there is currently no conclusive evidence to confirm or refute its validity. The cyclic model is one of many cosmological theories that aim to explain the origin and evolution of the universe, and scientific research is ongoing to test and refine these theories.
In conclusion, the cyclic model of the universe proposes a different perspective on the Big Bang and suggests that the universe may undergo cycles of expansion and contraction. While this theory challenges the traditional understanding of the universe’s origins, it is still a subject of debate and further investigation is needed to gather more evidence and refine our understanding of the universe’s past and future. Scientists continue to explore different cosmological models, including the cyclic model, to unravel the mysteries of the universe’s existence and its ultimate fate.
Eternal Life and the Fate of the Universe
Discussing the limitations of the universe and its inability to support eternal life
In exploring the ultimate fate of the universe, one must also consider the implications for life and the concept of eternal existence. While the universe itself may have various possible outcomes, it is crucial to acknowledge the limitations that prevent the existence of eternal life within our current understanding.
According to our current scientific understanding, the universe will undergo some form of change or transformation in the future. Whether it expands indefinitely, collapses into a singularity, or maintains a balanced state, these scenarios all point towards a finite existence for the universe itself.
While humans may strive for immortality or eternal life, the finite nature of the universe presents significant challenges. The physical laws and conditions necessary to sustain life, as we know it, may not persist indefinitely. The availability of resources, energy, and the stability of cosmic structures are all factors that influence the feasibility of eternal life.
Even if humanity were to overcome these challenges and find ways to extend life indefinitely, the eventual fate of the universe would render such efforts ultimately futile. The cosmic changes, such as the expansion or contraction, would inevitably lead to the disruption or destruction of any form of life that may have existed.
Examining the implications for humanity in light of the finite nature of the universe
The finite nature of the universe has profound implications for humanity and our understanding of our place in the cosmos. It highlights the importance of cherishing and making the most of our existence within the limited timeframe we have.
Knowing that the universe will not last forever encourages a sense of urgency and appreciation for the present moment. It prompts us to value human relationships, personal growth, and the pursuit of knowledge and experiences.
The finite nature of the universe also emphasizes the significance of leaving a lasting legacy. While our individual lives may be limited, the impact we can have on future generations and the world around us can endure beyond our time. It encourages us to strive for making a positive difference and contributing to the betterment of society and the world.
By acknowledging the finite nature of the universe and our existence within it, we can gain a deeper perspective on life’s meaning and purpose. It reminds us to focus on what truly matters and to live a life aligned with our values and aspirations.
In conclusion, the ultimate fate of the universe may be uncertain, with various possible outcomes suggested by general relativity. However, it is important to recognize that the finite nature of the universe imposes limitations on the concept of eternal life. While humans may strive for immortality, the cosmic changes that await the universe will inevitably disrupt any form of life that may exist. Understanding the finiteness of our universe prompts us to cherish the present moment, value human connections, and leave a lasting positive impact on the world around us.
Different Hypotheses on the Universe’s Future
Presenting various scientific hypotheses on the fate of the universe
Scientists have proposed several hypotheses regarding the ultimate destiny of the universe. These hypotheses offer various possibilities for the future of our cosmos, each with its own set of implications.
One hypothesis suggests that the universe may continue to expand indefinitely. This theory, known as the “Big Freeze” or “Heat Death,” suggests that over time, all matter and energy will become so dispersed that the universe will become cold and lifeless. In this scenario, stars would eventually burn out, and no new stars would be formed, leading to a desolate and dark universe.
Another hypothesis proposes a different fate for the universe, known as the “Big Crunch” or “Big Bounce.” According to this theory, the expansion of the universe will eventually slow down and reverse, causing it to collapse in on itself. This collapse would result in a singularity, where all the matter and energy in the universe would be compressed into an infinitely dense point. This scenario would potentially set the stage for a new universe to be born in a cosmic event known as the “Big Bounce.”
A third hypothesis suggests that the universe may maintain a balanced state between expansion and contraction. This theory, known as the “Big Balance” or “Big Freeze-Bounce,” proposes that the universe may oscillate between expansion and contraction, with each cycle beginning from a dense, hot state. In this scenario, the universe would undergo repeated cycles of expansion and contraction, potentially leading to the creation of new universes and the perpetuation of cosmic existence.
Considering different possibilities for the ultimate destiny of the universe
While these hypotheses offer different perspectives on the fate of the universe, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of our current scientific understanding. The true destiny of the universe remains uncertain, and further research and observations are needed to gain a more comprehensive understanding.
Regardless of the specific outcome, these hypotheses raise thought-provoking questions about the nature of existence and the potential for life in the universe. They prompt us to contemplate our place in the cosmic scheme and the significance of our existence within a vast and ever-changing universe.
As we continue to explore and push the boundaries of scientific knowledge, it is crucial to approach these hypotheses with an open mind and an appreciation for the complexity of the cosmos. The pursuit of understanding the ultimate fate of the universe broadens our perspective and fuels our curiosity towards unlocking the mysteries of the cosmos.
In conclusion, various scientific hypotheses offer different possibilities for the fate of the universe. Whether it expands indefinitely, collapses into a singularity, or undergoes a series of oscillations, these hypotheses highlight the immense complexity and uncertainty of the universe’s destiny. It is through continued scientific exploration and the collective efforts of researchers worldwide that we may one day unravel the true nature and ultimate fate of our universe.
Predicted Futures for the Universe
Exploring possible futures for the universe based on current scientific understanding
In the realm of scientific hypotheses, several predicted futures for the universe have been postulated. These predictions are based on our current understanding of the laws of physics and the observed behavior of celestial objects. While there is no definitive answer, scientists have offered various scenarios for the ultimate fate of the universe.
One possible future is the idea of the universe expanding indefinitely. This hypothesis suggests that the universe will continue to expand at an accelerated rate due to the influence of dark energy. Over time, galaxies would become increasingly distant from each other, and the universe would become colder and more dilute.
Conversely, another hypothesis proposes that the universe will eventually collapse into a singularity. This scenario, known as the “Big Crunch,” suggests that the universe’s expansion will reverse and gravitational forces will cause everything to return to a state of extreme density. This would result in the collapse of galaxies and the universe as a whole.
Yet another predicted future involves a balanced state for the universe, where the expansion gradually slows down but never reaches a point of collapse. In this scenario, known as the “Big Freeze” or “Heat Death,” the universe would eventually reach a state of maximum entropy, where all available energy is evenly distributed and no further work can be done. This would lead to a universe devoid of organized structures and the potential for life.
Examining finite and infinite scenarios for the universe’s existence
The concept of the universe’s existence can be explored from both finite and infinite perspectives. Some hypotheses postulate that the universe has existed for a finite amount of time, while others propose an infinite timeline.
If the universe has existed for a finite duration, it raises questions about its origin. Scientists have theorized that the universe began with the Big Bang, a rapid expansion from a singularity that occurred approximately 13.8 billion years ago. However, the ultimate cause or reason for this event remains unknown.
On the other hand, the idea of an infinite universe suggests that it has neither a beginning nor an end. This concept is based on the assumption that the laws of physics and the nature of space and time are inherently infinite. While difficult to grasp, an infinite universe would imply that there are an infinite number of galaxies and celestial bodies spread throughout space.
The debate between a finite and infinite universe raises philosophical and scientific questions about causality, time, and the nature of existence itself. While theoretical frameworks exist to explain both possibilities, definitive answers may lie beyond our current understanding of the universe.
In conclusion, the predicted futures for the universe are based on scientific hypotheses and our current understanding of the laws of physics. These include scenarios of indefinite expansion, eventual collapse, and a balanced state. Furthermore, the concept of the universe’s existence can be viewed from both finite and infinite perspectives, each raising its own set of questions and implications. While we may not have all the answers, continued exploration and scientific advancements are unlocking new insights into the ultimate fate and nature of our universe.
Conclusion
Summarizing the different theories on the fate of the universe
In summary, scientists have put forth several hypotheses regarding the ultimate fate of the universe. These predictions are based on our understanding of the laws of physics and the observed behavior of celestial objects. While there is no definitive answer, three main scenarios have been proposed:
1. The universe expanding indefinitely: This hypothesis suggests that the universe will continue to expand at an accelerated rate due to the influence of dark energy. Over time, galaxies would become increasingly distant from each other, and the universe would become colder and more dilute.
2. The universe collapsing into a singularity: Known as the “Big Crunch,” this scenario suggests that the universe’s expansion will reverse, and gravitational forces will cause everything to return to a state of extreme density. This would lead to the collapse of galaxies and the universe as a whole.
3. A balanced state of the universe: In this scenario, known as the “Big Freeze” or “Heat Death,” the expansion of the universe gradually slows down but never reaches a point of collapse. Eventually, the universe would reach a state of maximum entropy, where all available energy is evenly distributed, resulting in a lack of organized structures and potential for life.
Implications and potential advancements in our understanding of the universe’s destiny
The exploration of the fate of the universe raises intriguing questions and has profound implications for our understanding of the cosmos. By investigating the origin and destiny of the universe, scientists gain insights into the fundamental principles that govern our reality.
Advancements in technology and theoretical frameworks will continue to shape our understanding of the universe’s fate. Observations from space telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, provide valuable data that can further refine existing theories. Additionally, advancements in theoretical physics, such as the ongoing research on dark energy and the nature of spacetime, offer new avenues for exploration.
Understanding the fate of the universe also has implications for humanity’s place in the cosmos. It challenges us to contemplate our existence, the nature of time, and the possibility of other civilizations beyond our own. The quest to comprehend the universe’s destiny fuels curiosity, sparks philosophical debates, and drives advancements in scientific knowledge.
While definitive answers to the fate of the universe remain elusive, ongoing scientific efforts continue to contribute to the understanding of the cosmos. The lessons learned from exploring the fate of the universe deepen our appreciation for the vastness of space and the mysteries that await discovery.
In conclusion, the predictions for the fate of the universe are based on scientific hypotheses rooted in our current understanding of physics. These scenarios include indefinite expansion, eventual collapse, or a balanced state. The nature of the universe’s existence raises questions about its origin and whether it has a finite or infinite timeline. As we continue to advance our knowledge and technology, we strive towards unraveling the ultimate destiny and nature of our universe.